Well-being Index
A Well-being Index is a valuable tool for assessing and promoting the overall quality of life for individuals and communities. By providing a more nuanced understanding of well-being, it contributes to informed decision-making, effective policy implementation, and the creation of environments that support the flourishing of individuals and societies.
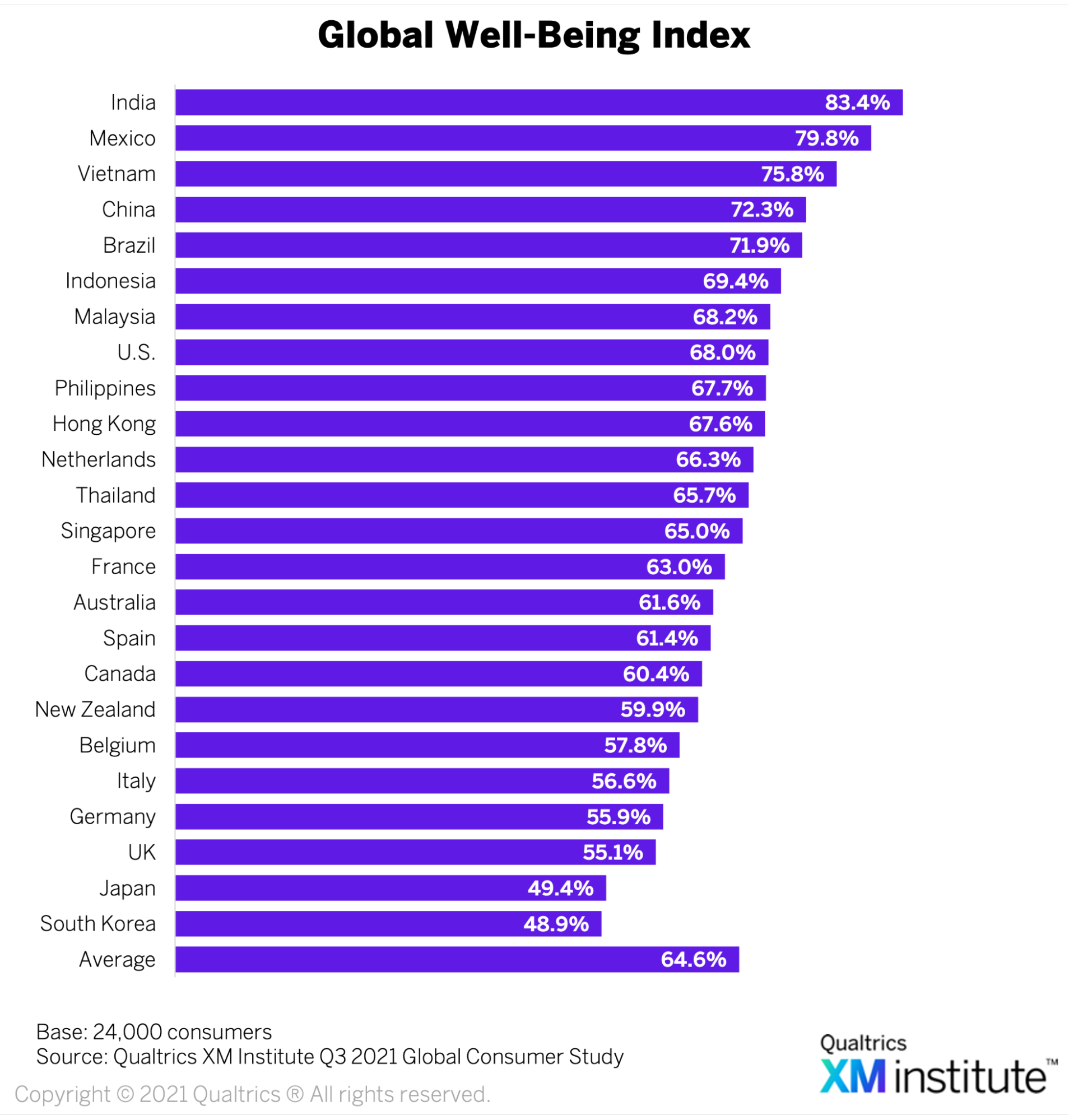
Need for Well-being index
Comprehensive Measurement
A Well-being Index provides a holistic and comprehensive measurement of individuals’ and communities’ overall well-being. It goes beyond purely economic indicators, such as GDP, to incorporate various aspects of life that contribute to overall happiness and satisfaction.
Policy Guidance
Governments and policymakers can use a Well-being Index to guide the development and implementation of policies that positively impact the well-being of their citizens. This can include policies related to healthcare, education, social support, and environmental sustainability.
Public Awareness and Advocacy
A Well-being Index raises public awareness about the importance of well-being and provides a benchmark for advocacy efforts. It helps citizens and organizations advocate for policies and practices that prioritize well-being over purely economic measures.
Resource Allocation
By assessing well-being across different regions or demographic groups, a Well-being Index assists in the allocation of resources to address disparities and improve the quality of life for those who may be at a disadvantage.
Long-term Planning
A Well-being Index aids in long-term planning by identifying trends and patterns in well-being over time. This information is crucial for anticipating challenges and designing sustainable solutions for the future.
International Comparisons
Countries can use Well-being Index rankings to compare themselves on a global scale. This can foster healthy competition and encourage the sharing of best practices to improve overall well-being worldwide.
Corporate and Organizational Benefits
Companies and organizations can adopt well-being indices to assess the well-being of their employees. This can lead to improved workplace environments, increased employee satisfaction, and potentially higher productivity.
Research and Academic Purposes
Well-being Indices contribute to academic research by providing a standardized measure for studying the impact of various factors on individuals’ well-being. Researchers can use the index to explore trends, correlations, and causation.
Prevention and Intervention
A Well-being Index can help identify areas where intervention is needed to prevent negative outcomes. For example, if mental health indicators are low in a particular community, targeted interventions can be implemented to address this issue proactively.
Public Health and Sustainable Development
Well-being is closely tied to public health and sustainable development. A Well-being Index can guide strategies for achieving sustainable development goals by considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
1.
Comprehensive Measurement
A Well-being Index provides a holistic and comprehensive measurement of individuals’ and communities’ overall well-being. It goes beyond purely economic indicators, such as GDP, to incorporate various aspects of life that contribute to overall happiness and satisfaction.
Policy Guidance
Governments and policymakers can use a Well-being Index to guide the development and implementation of policies that positively impact the well-being of their citizens. This can include policies related to healthcare, education, social support, and environmental sustainability.
2.
3.
Public Awareness and Advocacy
A Well-being Index raises public awareness about the importance of well-being and provides a benchmark for advocacy efforts. It helps citizens and organizations advocate for policies and practices that prioritize well-being over purely economic measures.
Resource Allocation
By assessing well-being across different regions or demographic groups, a Well-being Index assists in the allocation of resources to address disparities and improve the quality of life for those who may be at a disadvantage.
4.
5.
Long-term Planning
A Well-being Index aids in long-term planning by identifying trends and patterns in well-being over time. This information is crucial for anticipating challenges and designing sustainable solutions for the future.
International Comparisons
Countries can use Well-being Index rankings to compare themselves on a global scale. This can foster healthy competition and encourage the sharing of best practices to improve overall well-being worldwide.
6.
7.
Corporate and Organizational Benefits
Companies and organizations can adopt well-being indices to assess the well-being of their employees. This can lead to improved workplace environments, increased employee satisfaction, and potentially higher productivity.
Research and Academic Purposes
Well-being Indices contribute to academic research by providing a standardized measure for studying the impact of various factors on individuals’ well-being. Researchers can use the index to explore trends, correlations, and causation.
8.
9.
Prevention and Intervention
A Well-being Index can help identify areas where intervention is needed to prevent negative outcomes. For example, if mental health indicators are low in a particular community, targeted interventions can be implemented to address this issue proactively.
Public Health and Sustainable Development
Well-being is closely tied to public health and sustainable development. A Well-being Index can guide strategies for achieving sustainable development goals by considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
